Arduino Project 030A - Dual Motor Driver L298N
L298N Dual Motor Driver Project Description
The L298N Motor Driver is a controller that uses an H-Bridge to easily control motors direction and PWM to control the speed. This module allows you to independently manage two motors of up to 2A each in both directions. Supply range may vary between 5V and 35V, enough for most DC motor projects.
In first place, let's understand the meaning of each pin provided on L298N board.
L298N Pinout
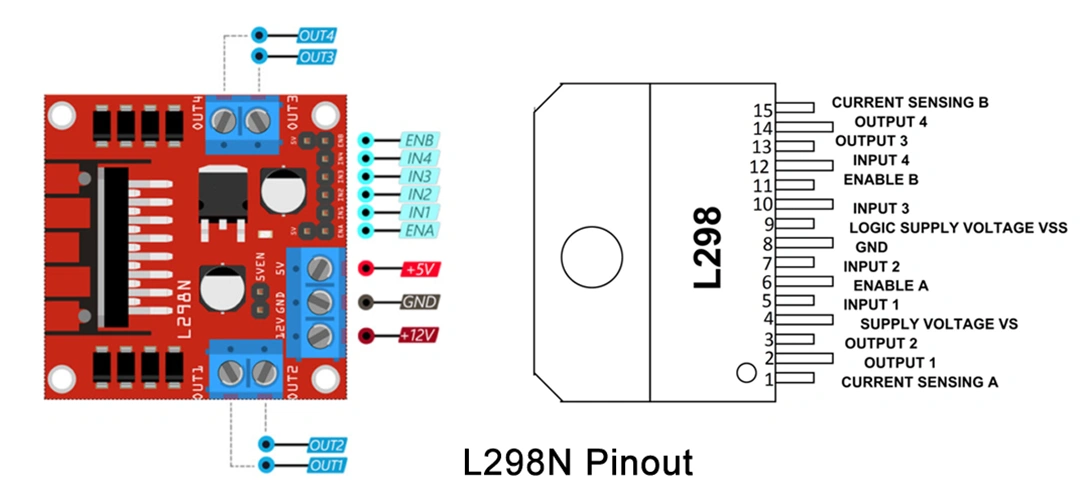
The spinning direction of the motor can be controlled by applying logic HIGH or logic LOW to IN1/IN2 (motor A) and IN3/IN4 (motor B) inputs as shown on table.
The speed control pins ENA and ENB are used to turn on/off the motors and control their speed with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). That means that motor will spin at full speed with HIGH and stop with LOW. Usually the module comes with a jumper on these pins that connects them directly to HIGH value. If you want to keep the speed control of your motors remove the jumper and connect ENA and/or ENB pins to PWM. Otherwise the motor will always spin at full speed.
Voltage regulator
The module includes 5V regulator that can be enabled/disabled using a jumper:
-
With jumper: the regulator is enabled and +5V pin acts as output. It can be used to power an Arduino or other circuitry that needs 5V power. Note: with power supply greater than 12V the jumper must be removed to prevent damage to the onboard regulator.
-
Without jumper: the regulator is disabled and +5V pin acts as input, expecting 5V to be supplied.
Take into consideration that the L298N module has voltage drop of approximately 2V. With 12V power supply the motors will receive approximately 10V which means that we won't be able to get the maximum speed.
Circuit and Schematic
Having a solid understanding of each pin and how the module works we can proceed with the wiring.
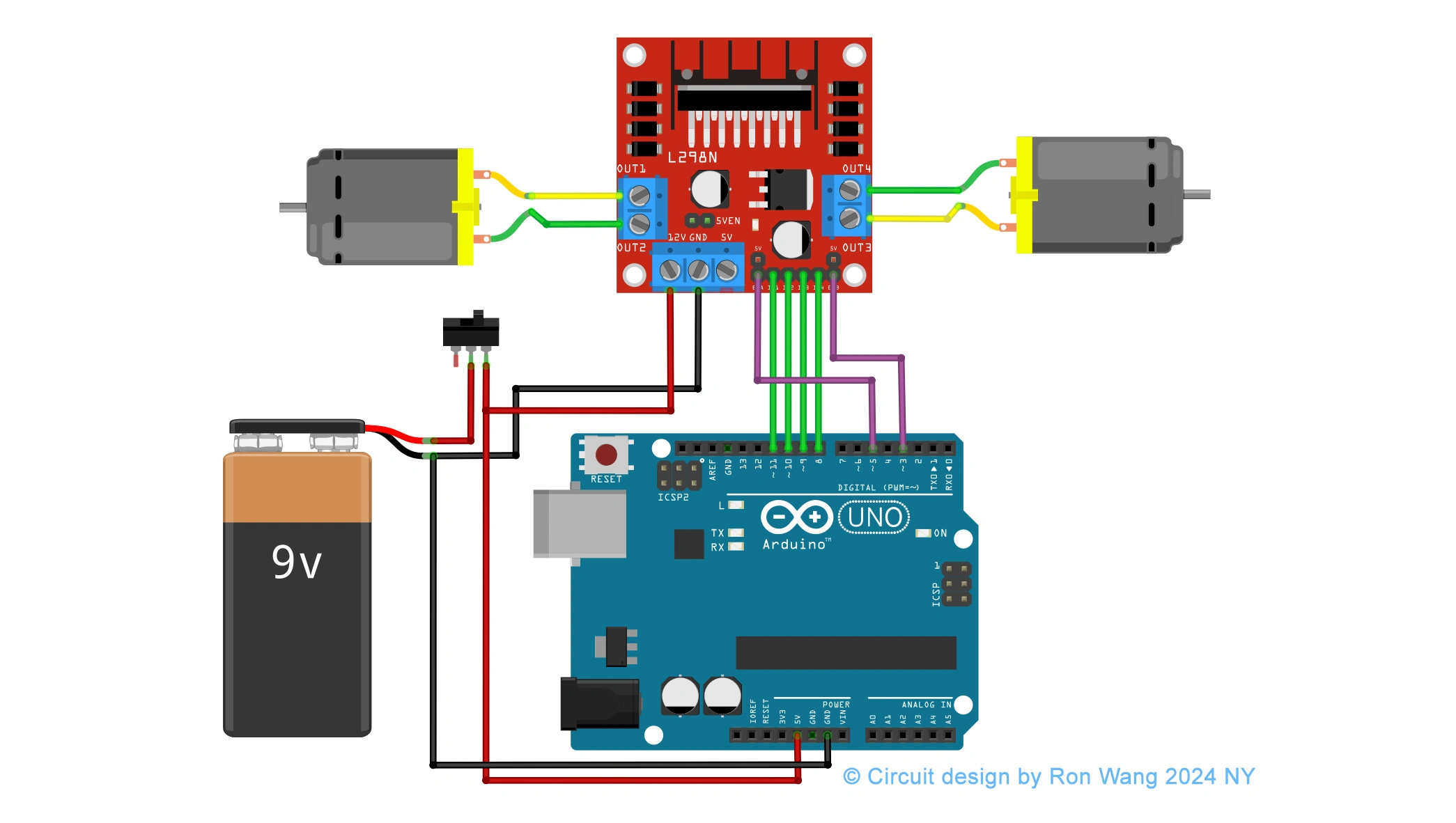
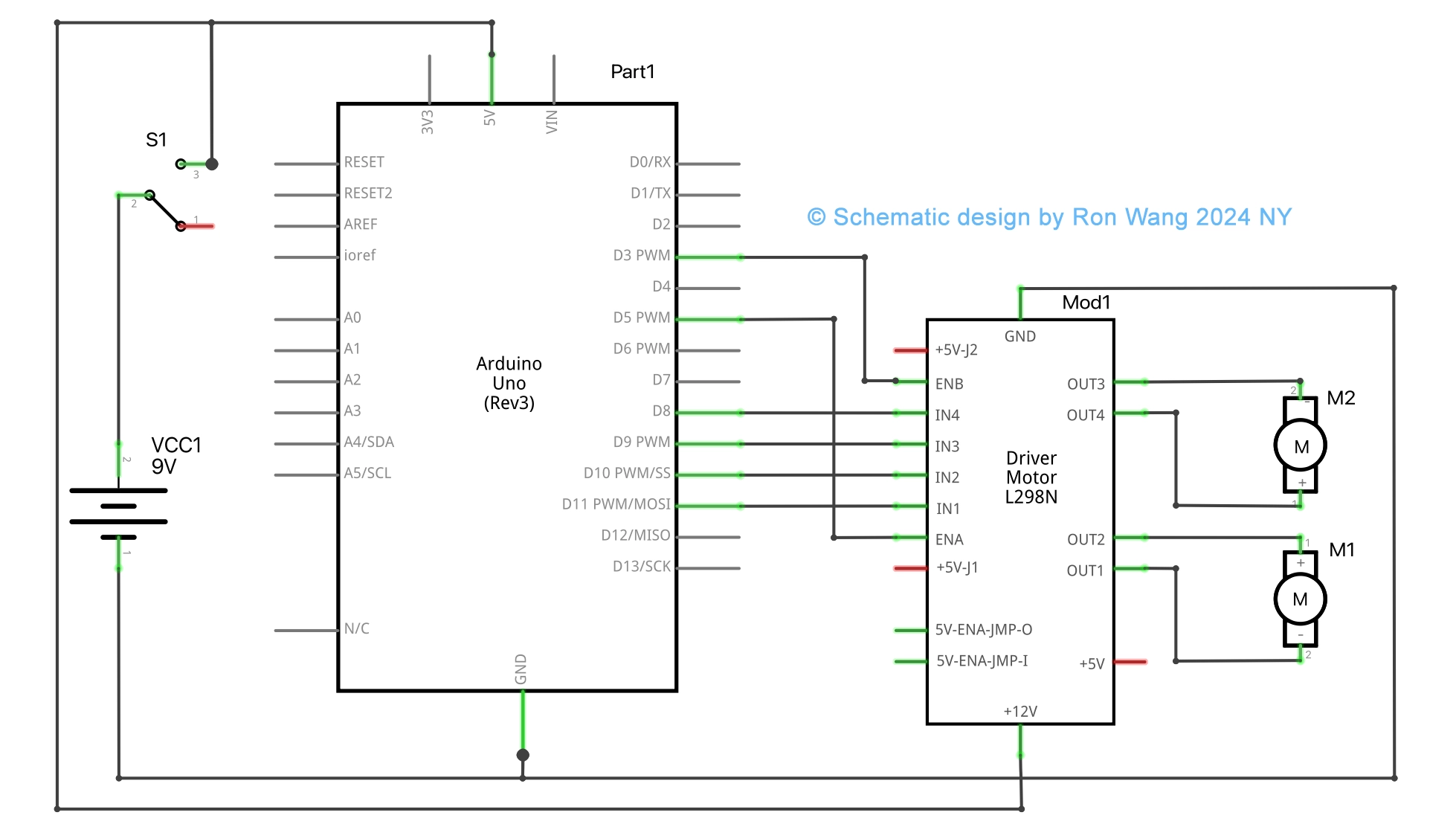
Coding
// Motor A
#define ENA_PIN 5 //PWM
#define IN1_PIN 10
#define IN2_PIN 11
// Motor B
#define ENB_PIN 3 //PWM
#define IN3_PIN 8
#define IN4_PIN 9
struct motor {
byte speed = 0;
struct {
byte input1 = LOW;
byte input2 = LOW;
} direction;
};
motor motorA, motorB;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
// Set PWM & direction pins to output for both motor
pinMode(ENA_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN1_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENB_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN3_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN4_PIN, OUTPUT);
// Init with default values
sendToMotorA();
sendToMotorB();
}
void loop()
{
Serial.println("Motors are stopped now");
Serial.println("Set direction FORWARD");
delay(2000);
setMotorDirectionForward(motorA);
setMotorDirectionForward(motorB);
Serial.println("Gradually increase motors speed to max");
increaseMotorsSpeed();
Serial.println("Motors are on full speed now");
delay(2000);
Serial.println("Gradually decrease motors speed to min");
decreaseMotorsSpeed();
Serial.println("Motors are stopped now");
Serial.println("Set direction BACKWARD");
delay(2000);
setMotorDirectionBackward(motorA);
setMotorDirectionBackward(motorB);
Serial.println("Gradually increase motors speed to max");
increaseMotorsSpeed();
Serial.println("Motors are on full speed now");
delay(2000);
Serial.println("Gradually decrease motors speed to min");
decreaseMotorsSpeed();
}
void sendToMotorA()
{
sendToMotor(motorA, ENA_PIN, IN1_PIN, IN2_PIN);
}
void sendToMotorB()
{
sendToMotor(motorB, ENB_PIN, IN3_PIN, IN4_PIN);
}
void increaseMotorsSpeed()
{
for (int speed = 0; speed <= 255; speed++) {
setMotorSpeed(motorA, speed);
setMotorSpeed(motorB, speed);
sendToMotorA();
sendToMotorB();
delay(20); // Add small delay between changes
}
}
void decreaseMotorsSpeed()
{
for (int speed = 255; speed >= 0; speed--) {
setMotorSpeed(motorA, speed);
setMotorSpeed(motorB, speed);
sendToMotorA();
sendToMotorB();
delay(20); // Add small delay between changes
}
}
版权声明:本文为原创文章,版权归donstudio所有,欢迎分享本文,转载请保留出处!